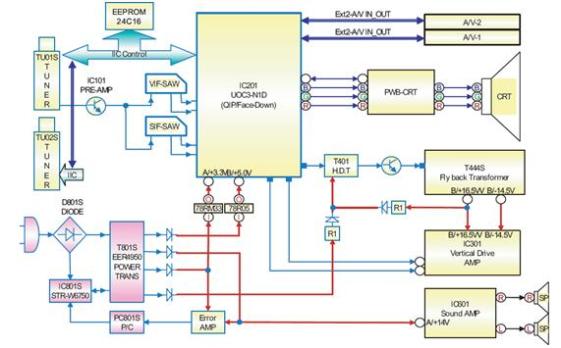
Transformer is an electrical device which can move and change the electric energy from one or more electrical circuits to another through a magnetic holding and based on the electromagnetic inductions principles. The purpose of transformer is to transmit and distribute power in AC rather than in DC. The reason is, because transformer does not work in DC so there must be some difficulties to transmit power in DC.
 Figure 1.1 The Energy Transformation
Figure 1.1 The Energy Transformation
- Transformer Principle
The basic principle of transformer is the mutual induction between two circuits which is connected by magnetic flux. Furthermore, transformer is consist of two induction coils which are separated in electrical way, but in magnetic way they are connected by a path .
When the primary coil of a transformer is connected to an alternating voltage, there will be a current in the primary coil called the exciting current. The exciting current sets up an alternating flux which links the turns and induces a voltage on both windings.
- Transformer Symbols
Figure 2.1 The Transformer Symbols
- Transformer Applications and Uses
There are several applications and uses of transformer which are very important.
- Transformer can increase or decrease the level of Voltage or Current in AC circuit. In addition, when the voltage is increasing, the current will be decreasing and vice verse. Because P=V.I with the same power
- The value of capacitor, inductor, or even resistance in AC circuit can be increased or decreased by the transformer. It also can act as the impedance transferring device.
- Transformer can be used to prevent DC from passing one circuit to the others.
- It can isolate two circuits electrically.
The main application of transformer is to Step up (increasing) or Step down (decreasing) the voltage level. Without transformers the widespread distribution of electrical power would be impractical. Transformers make it possible to generate power at a convenient voltage, step up to a very high voltage for long distance transmission, and then step down for practical distribution.
References
Petruzella (1996). Industrial Electronics.Singapore: McGraw Hill.
Electrical Technology.(2012, February). Uses and Application of Transformer. Accessed on May 1st 2014, From http://www.electricaltechnology.org/2012/02/uses-and-application-of-transformer.html
Website Staff UI (2010).TRANSFORMER PAPERS. Accessed on May 1st 2014, from staff.ui.ac.id/system/files/users/…/transformerpaper.pdf
http://www.g3npf.co.uk/transformers.htm